The Eumetsat LSA SAF (Land Surface Analysis Application Facility) is generating products from MSG and Metop satellites, allowing to characterize and to monitor land surfaces. The data is available in Near Real Time (NRT) and Climate Data Records for some products are also available, enabling homogeneous time series analysis of several parameters. LSA SAF products are produced since 2004, at different time frequencies: from 15 min, for the case of MSG derived products, to daily and ten daily, for Metop based products.
From the set of products produced by the LSA SAF, the vegetation products, such as NDVI and fAPAR enable to characterize the vegetation conditions.
The ENDVI (EPS NDVI) are near-global, 10-daily composite images which are synthesized from the "best available" observations registered in the course of every "dekad" by the orbiting earth observation system Metop-AVHRR.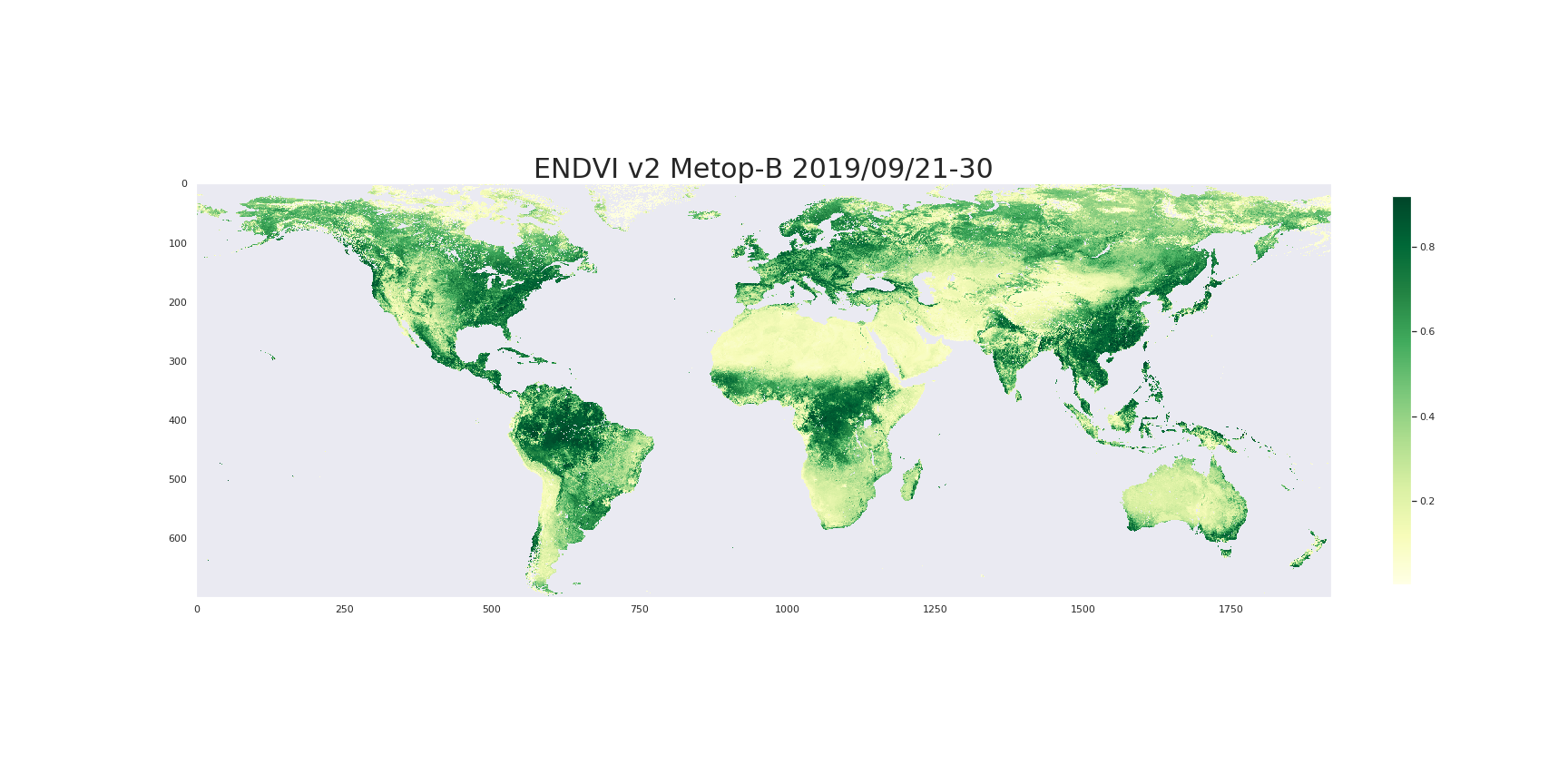
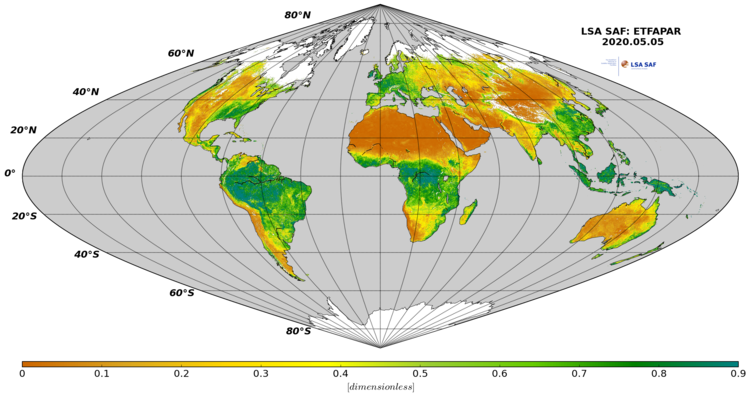
Fraction of Absorbed Photosynthetically Active Radiation (FAPAR) defines the fraction of PAR (400-700 nm) absorbed by the green parts of the canopy, and thus expresses the canopy's energy absorption capacity. FAPAR depends both on canopy structure, leaf and soil optical properties and irradiance conditions. FAPAR has been recognized as one of the fundamental terrestrial state variables in the context of the global change sciences (Steering Committee for GCOS, 2003; Gobron et al., 2006). It is a key variable in models assessing vegetation primary productivity and, more generally, in carbon cycle models implementing up-to-date land surfaces process schemes. Besides, FAPAR it is an indicator of the health of vegetation. FAPAR is generally well correlated with the LAI, the more for healthy fully developed vegetation canopies.
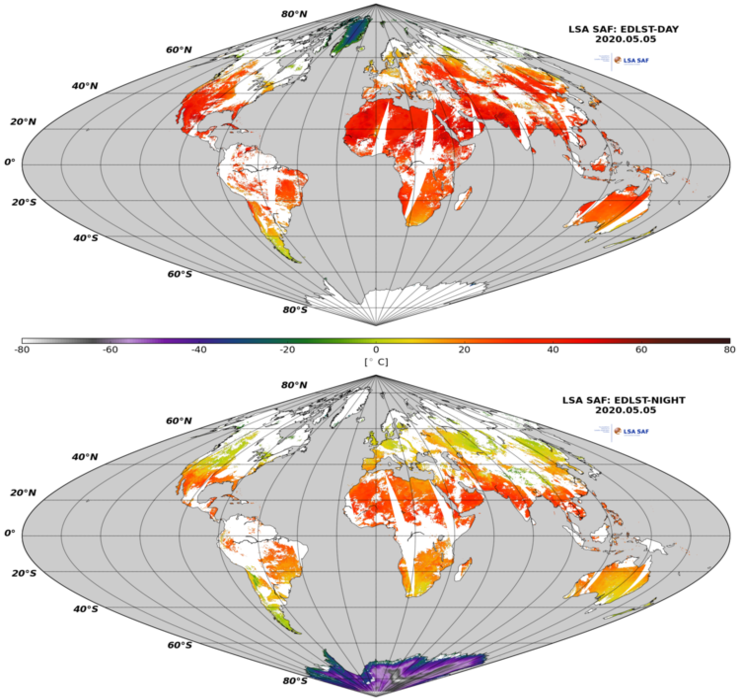
Many wild fires are anticipated by extreme warm conditions. Maps of Land Surface Temperature allows to evaluate the extent of regions affected by very high temperatures.
The EDLST (EPS Daily Land Surface Temperature) provides a day-time and nigh-time retrievals of LST based on clear-sky measurements from the Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer (AVHRR) on-board EUMETSAT polar system satellites, the Metop series.
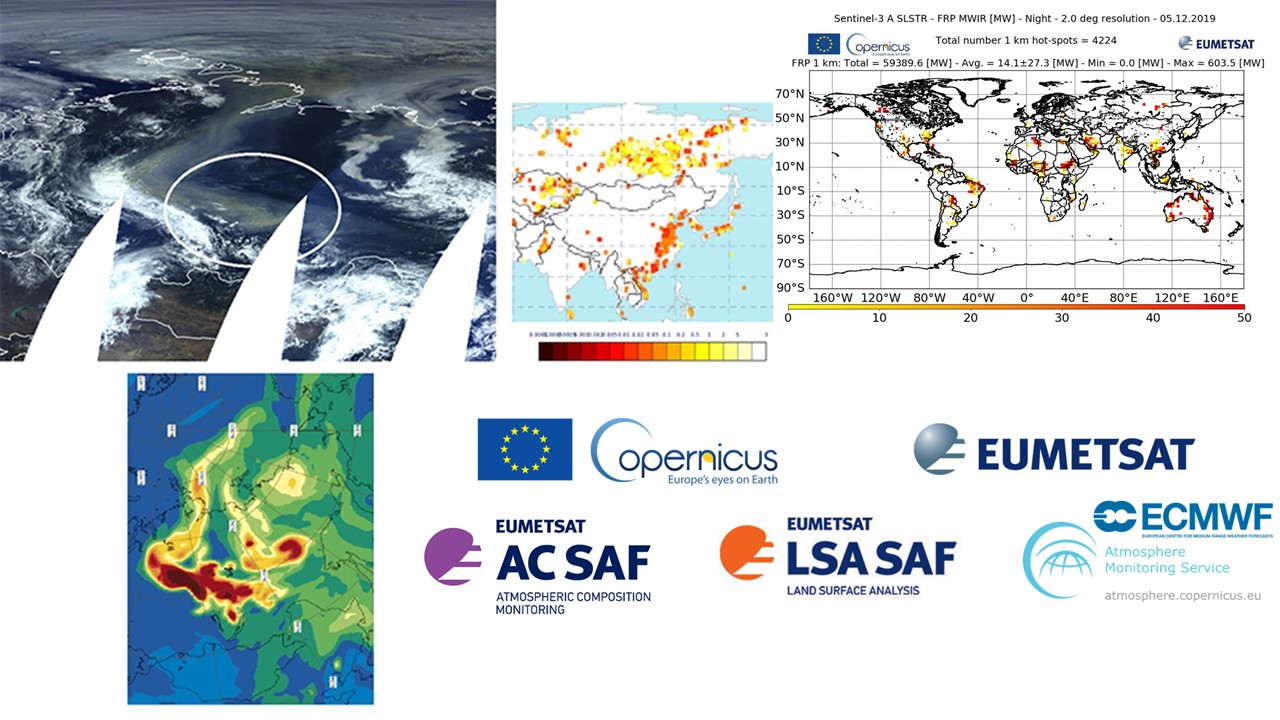
Fires location and intensity can be followed with the LSA SAF Fire Radiative Power (FRP) product, base on MSG observations.
The FRP product records information on the location, timing and fire radiative power (MWatts) output of landscape fires detected every 15 minutes across the full Meteosat disk at the native spatial resolution of the SEVIRI sensor. Measuring this FRP and integrating it over the lifetime of a fire provides an estimate of the total Fire Radiative Energy (FRE) released, which for landscape fires should be proportional to the total amount of biomass burned.